Vacuole Drawing
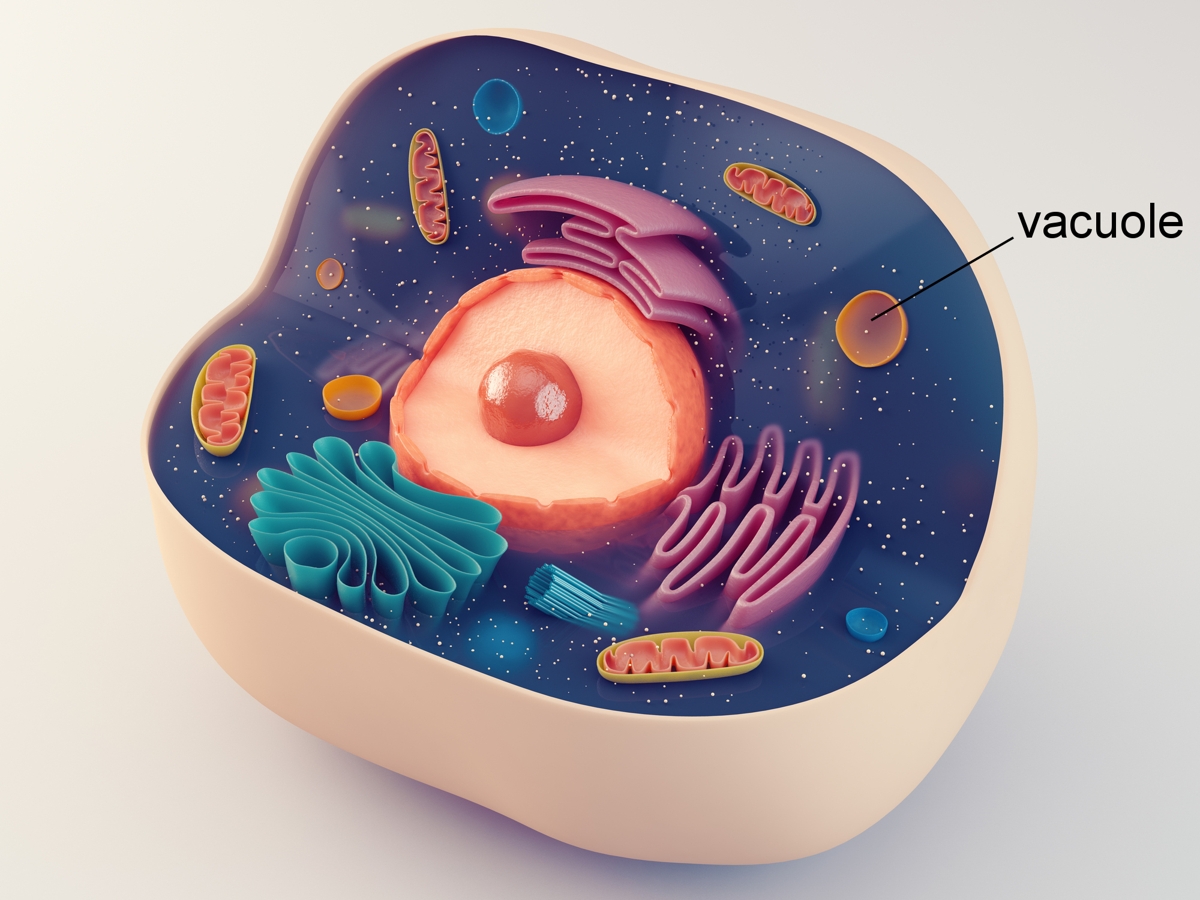
Vacuole Drawing - However, some protists , animal cells, and bacteria also contain vacuoles. This figure show the major organelles and other cell components of a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Vector illustration of the basic structure of. Nucleolus nucleus ribosome (dots as part of 5) vesicle rough endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus (or, golgi body) cytoskeleton smooth endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion vacuole cytosol (fluid that contains organelles; Diagram of a cell with multiple small vacuoles (above) and a large central vacuole (below).
Web the central vacuole contributes to the plant’s overall structure by drawing in water, inflating the cell to a turgid state (more on this in lab 5). The mechanism keeps the plant from wilting and. Web plant cells have cell walls that surround their cell membrane, and large central vacuoles that make the cell rigid. With which, comprises cytoplasm) lysosome centrosome cell. Additionally, animal cells usually have an irregular shape, while plant cells are more rectangular. As mentioned above, the water there pushes the cytoplasm outward against the cell wall. The cell wall, nucleus, and chloroplasts are visible.
Vacuole Main Function In Plant Cell
Nucleolus nucleus ribosome (dots as part of 5) vesicle rough endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus (or, golgi body) cytoskeleton smooth endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion vacuole cytosol (fluid that contains organelles; Vector illustration of the basic structure of. Web the central vacuole is a large organelle that often fills most of the plant cell. Most popular bacteria seamless.
Vacuole Function and Structure Extra Space Storage Rs' Science
This figure show the major organelles and other cell components of a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Both plant and fungal cells contain vacuoles, but plant cells typically have a single large central vacuole, while fungal cells have several smaller vacuoles. Plant cells grow by dividing and expanding in all directions. It is filled with liquid.
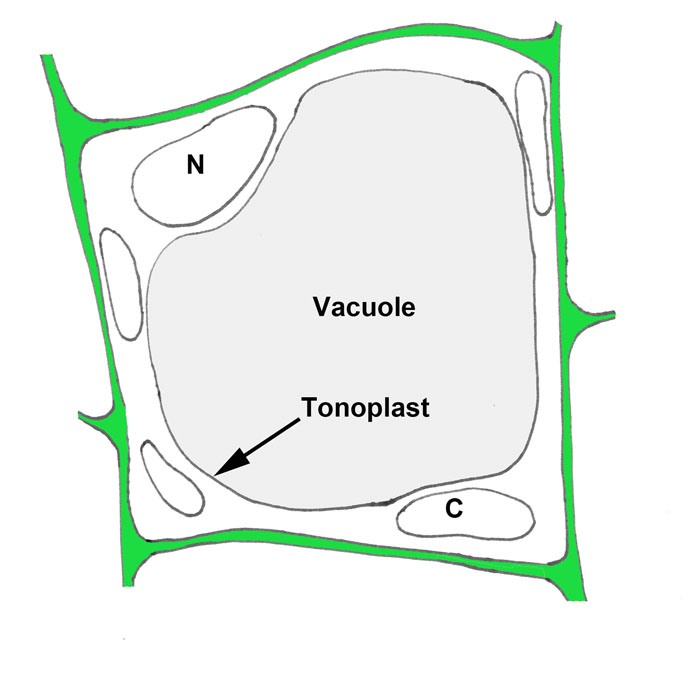
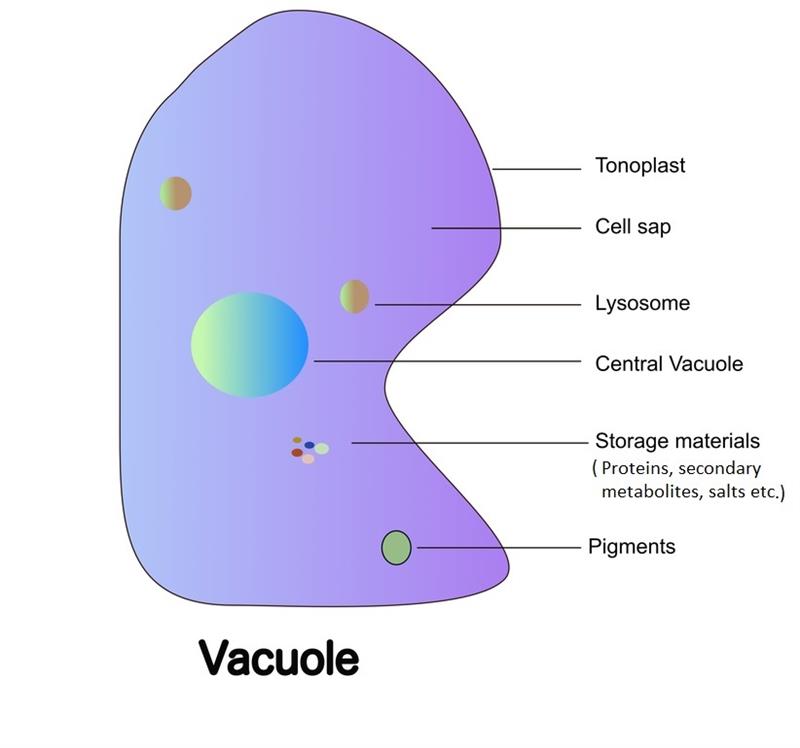
Explain the structure of the vacuole.
Web the central vacuole of a plant has a crucial role. Cell wall, cytoplasm, and chloroplasts. Web updated on january 08, 2020 a vacuole is a cell organelle found in a number of different cell types. They are found mostly in plant cells and fungi. However, they differ in certain aspects. Web a vacuole is.
Vacuoles — lesson. Science CBSE, Class 9.
Web plant cells have cell walls that surround their cell membrane, and large central vacuoles that make the cell rigid. Web a vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials. As mentioned above, the water there pushes the cytoplasm outward against the cell wall. The cell wall, nucleus, and.
An Introduction to Vacuole Organelles
Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system (figure \(\pageindex{1. Above is a cell from the aquatic plant elodea. Additionally, animal cells usually have an irregular shape, while plant cells are more rectangular. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other.
An Introduction to Vacuole Organelles
This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted, and those that have been phagocytized, or engulfed, by the cell. Web the central vacuole contributes to the plant’s overall structure by drawing in water, inflating the cell to a turgid state (more on this in lab 5). With which, comprises cytoplasm).
What Is a Vacuole? Understanding the 4 Main Functions
Plant cells grow by dividing and expanding in all directions. See vacuole stock video clips filters all images photos vectors illustrations 3d objects sort by popular a mature cell vacuole. Diagram of a cell with multiple small vacuoles (above) and a large central vacuole (below). Especially in protozoa, vacuoles are cytoplasmic organs, performing functions such.
How to draw vacuole Labelled Biology Diagrams of vacuole by Hajong
Web updated on january 08, 2020 a vacuole is a cell organelle found in a number of different cell types. Plant cells grow by dividing and expanding in all directions. Web animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes, cytoskeletons, and mitochondria. Vector illustration of the basic structure of. With which, comprises cytoplasm).
1.11 Vacuoles Biology LibreTexts
The vacuole is surrounded by the tonoplast membrane. Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system (figure \(\pageindex{1. Web the central vacuole contributes to the plant’s overall structure by drawing in water, inflating the cell to a turgid state (more on this in lab 5). For example, plant cells have a cell wall.
Vacuole Facts Biology Wise
The plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, plastids, and a central vacuole—structures not in animal cells. Both plant and fungal cells contain vacuoles, but plant cells typically have a single large central vacuole, while fungal cells have several smaller vacuoles. Diagram of a cell with multiple small vacuoles (above) and a large central vacuole.
Vacuole Drawing However, some protists , animal cells, and bacteria also contain vacuoles. Web plant cells have cell walls that surround their cell membrane, and large central vacuoles that make the cell rigid. Web animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes, cytoskeletons, and mitochondria. With which, comprises cytoplasm) lysosome centrosome cell. Web a vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials.
Vector Illustration Of The Basic Structure Of.
The vacuole is surrounded by the tonoplast membrane. The mechanism keeps the plant from wilting and. It is filled with liquid and surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast. Web animal cell diagram components of a typical animal cell:
Above Is A Cell From The Aquatic Plant Elodea.
For example, plant cells have a cell wall and a central vacuole, while animal cells contain centrosomes. A center portion of the cell within the cytoplasm appears clear. This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted, and those that have been phagocytized, or engulfed, by the cell. Most popular vector illustration of the plant cell anatomy structure.
Illustration Of The Plant Cell Anatomy Structure.
Plant cells grow by dividing and expanding in all directions. Cell wall, cytoplasm, and chloroplasts. Animal cells have neither of these structures. Nucleolus nucleus ribosome (dots as part of 5) vesicle rough endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus (or, golgi body) cytoskeleton smooth endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion vacuole cytosol (fluid that contains organelles;
They Are Found Mostly In Plant Cells And Fungi.
The cell wall, nucleus, and chloroplasts are visible. Plants can alter the solute concentration in the central vacuole to influence cell structure and movement of water. However, they differ in certain aspects. This figure show the major organelles and other cell components of a typical eukaryotic plant cell.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2000px-Plant_cell_structure_svg_vacuole.svg-58a886443df78c345bf8d009.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/plant-cell-structure--membrane--vacuole--centrosome--chloroplasts--nucleus--nucleolus--drawing-722209195-59fb25bc83ca58001ae4f902.jpg)