Power Of Point Theorem
Power Of Point Theorem - The radical axis is a line perpendicular to the line connecting the circles' centers (line ). Web power of a point theorem. We discard the negative solution since distance must be positive. For this to work, the functions defined by the power series must be continuous at , as you. (arml) in a circle, chords ab and cd intersect at r.
We have pow!(p) < 0 7.(radical axis) given two circles ! We have pow!(p) = (x a)2 + (y b)2 c2: Given a circle of radius 𝑟 centered at 𝑀 and a point 𝐴, the power of point 𝐴 with respect to circle 𝑀, denoted by 𝑃 ( 𝐴) , is given by 𝑃 ( 𝐴) = 𝐴 𝑀 − 𝑟. If p is a point, and k(o, r) is a circle with center o and radius. Let \(\omega\) be a circle and \( p\) a point. Given a point p and a circle, pass two lines through p that intersect the circle in points a and d and, respectively, b and c. (power of a point) if a line drawn through point p intersects circle at points a and b, then.
Circle Geometry Example 6 Power of a point YouTube
The power of a point theorem is a relationship that holds between the lengths of the line segments formed when two lines intersect a circle and each other. The radical axis is a line perpendicular to the line connecting the circles' centers (line ). ( p) = p 2 − r 2. Given a circle.
Power of a point Proof by Geometry way YouTube
12k views 6 years ago geometry. Powγ(p) = p2 −r2 (1) (1) pow γ. We claim that the two de nitions of the power of a point are equivalent. If the two circles intersect at two common points, their radical axis is the line through these two points. This is also known as the intersecting.
Question Video Using the Power of a Point Theorem for Two Secants to
You'll start by deriving the central angle theorem and thales' theorem, then move on to the power of a point theorem, and conclude with an exploration of different types of triangle centers and their presence on the euler line. Web value if pa and pb point in the same direction, and a negative value if.
GEOMETRY 28 Power of a Point with respect to a Circle YouTube
Find the value of in the following diagram: The power of a point theorem is a relationship that holds between the lengths of the line segments formed when two lines intersect a circle and each other. We have pow!(p) < 0 7.(radical axis) given two circles ! Which is the power of p. If the.
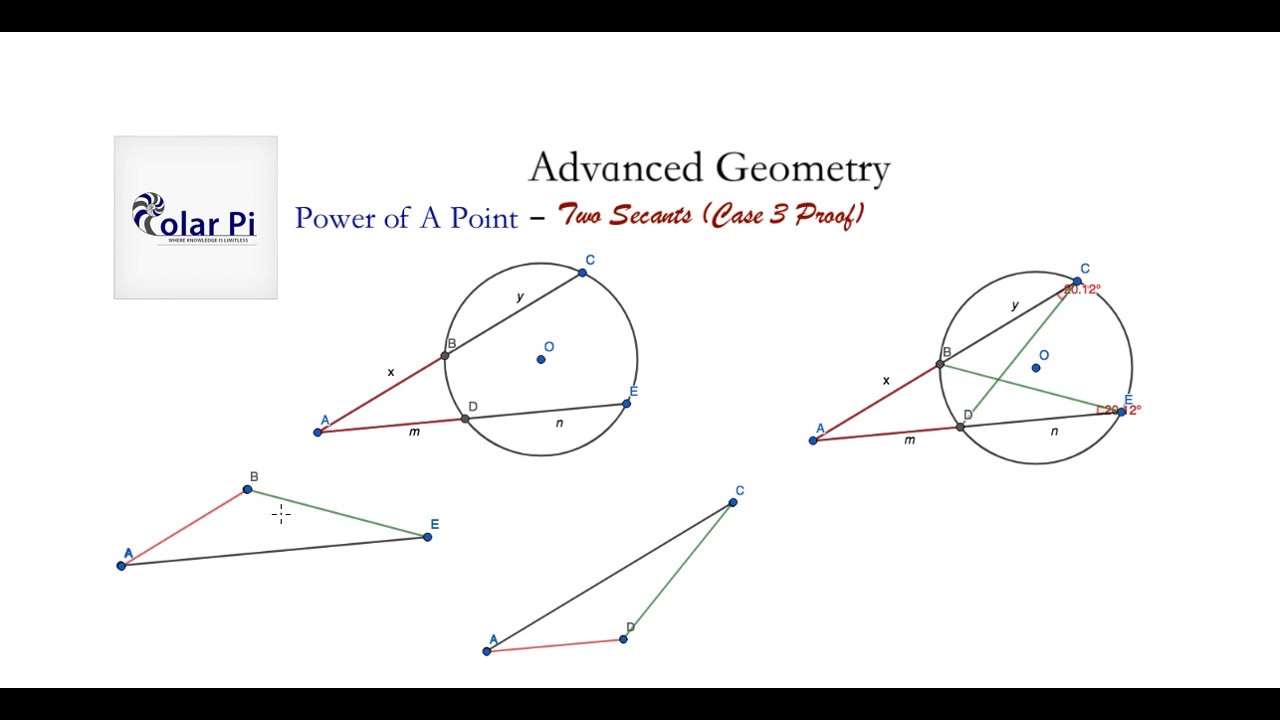
(The Power of A Point) Proof of Case 3 YouTube
Resources aops wiki power of. Web the proposition is identical to saying that if, for all in a neighbourhood of 0, we have: We have pow!(p) = (x a)2 + (y b)2 c2: Given a circle of radius 𝑟 centered at 𝑀 and a point 𝐴, the power of point 𝐴 with respect to the.
Theorem of the Day
There are two cases to this theorem; R in the plane, then op 2 r2 is called the power of p with respect to k. So the power of a point theorem says that the this quantity equals to pc pd, where c and d are the intersection with of any line through p. You'll.
Lesson The Power of a Point Theorem Nagwa
The power of a point theorem is a relationship that holds between the lengths of the line segments formed when two lines intersect a circle and each other. Powγ(p) = p2 −r2 (1) (1) pow γ. Back to the power of a point theorem. Given a point p and a circle, pass two lines through.
Question Video Using the Power of a Point Theorem for a Tangent and a
The power of a point theorem is a relationship that holds between the lengths of the line segments formed when two lines intersect a circle and each other. We have pow!(p) < 0 7.(radical axis) given two circles ! Given a circle of radius 𝑟 centered at 𝑀 and a point 𝐴, the power of.
Power Of A Point Formulas GeoGebra
In elementary plane geometry, the power of a point is a real number that reflects the relative distance of a given point from a given circle. 508 views 2 years ago classical geometry. 12k views 6 years ago geometry. If p 𝑀 of 𝐴 is equal to zero, then 𝐴 lies on the circle. If.
Power of a Point Theorem YouTube
There are two cases to this theorem; Web power of a point theorem/introductory problem 1. Which is the power of p. The power of a point theorem is a useful result in euclidean geometry about lengths. Where r r is the circle's radius, and p p is the distance from p p to the circle's.
Power Of Point Theorem This course covers a wide range of theorems in classical euclidean geometry. Proof (equivalence of de nition of the power of a point) A b p o a b p o by convention, the power of p is negative when p is inside the circle, and positive when p is outside the circle. Then all the coefficients are zero. If p 𝑀 of 𝐴 is equal to zero, then 𝐴 lies on the circle.
Find The Value Of In The Following Diagram:
We have pow!(p) = (x a)2 + (y b)2 c2: It was introduced by jakob steiner in 1826. In this video, i went over the 3 main types of power of a point problems. Given a circle of radius 𝑟 centered at 𝑀 and a point 𝐴, the power of point 𝐴 with respect to circle 𝑀, denoted by 𝑃 ( 𝐴) , is given by 𝑃 ( 𝐴) = 𝐴 𝑀 − 𝑟.
We Have Pow!(P) > 0, When P Is On !
We discard the negative solution since distance must be positive. There are two cases to this theorem; Web power of a point theorem. This course covers a wide range of theorems in classical euclidean geometry.
If P 𝑀 Of 𝐴 Is Equal To Zero, Then 𝐴 Lies On The Circle.
The radical axis is a line perpendicular to the line connecting the circles' centers (line ). If p 𝑀 of 𝐴 is greater than zero, then 𝐴 lies outside the circle. Web which is the power of p. Web the power of a point is used to find lengths of geometric figures involving circles.
Web Power Of A Point Theorem/Introductory Problem 1.
Applying the power of a point theorem, we get. Web value if pa and pb point in the same direction, and a negative value if they point in opposite directions. Web power of a point, explained. Then papb = (po + oa)(po + ob) = (po r)(po + r) = po2 r2;