Active Transport Drawing
Active Transport Drawing - No energy is necessary for this mode of transport. Passive transport does not use energy to transport molecules across the membrane. Web two major classes of facilitated transport proteins are channels and carrier proteins. This exports three sodium ions in return for two potassium ions. At activity end, administer the cell membrane quiz.
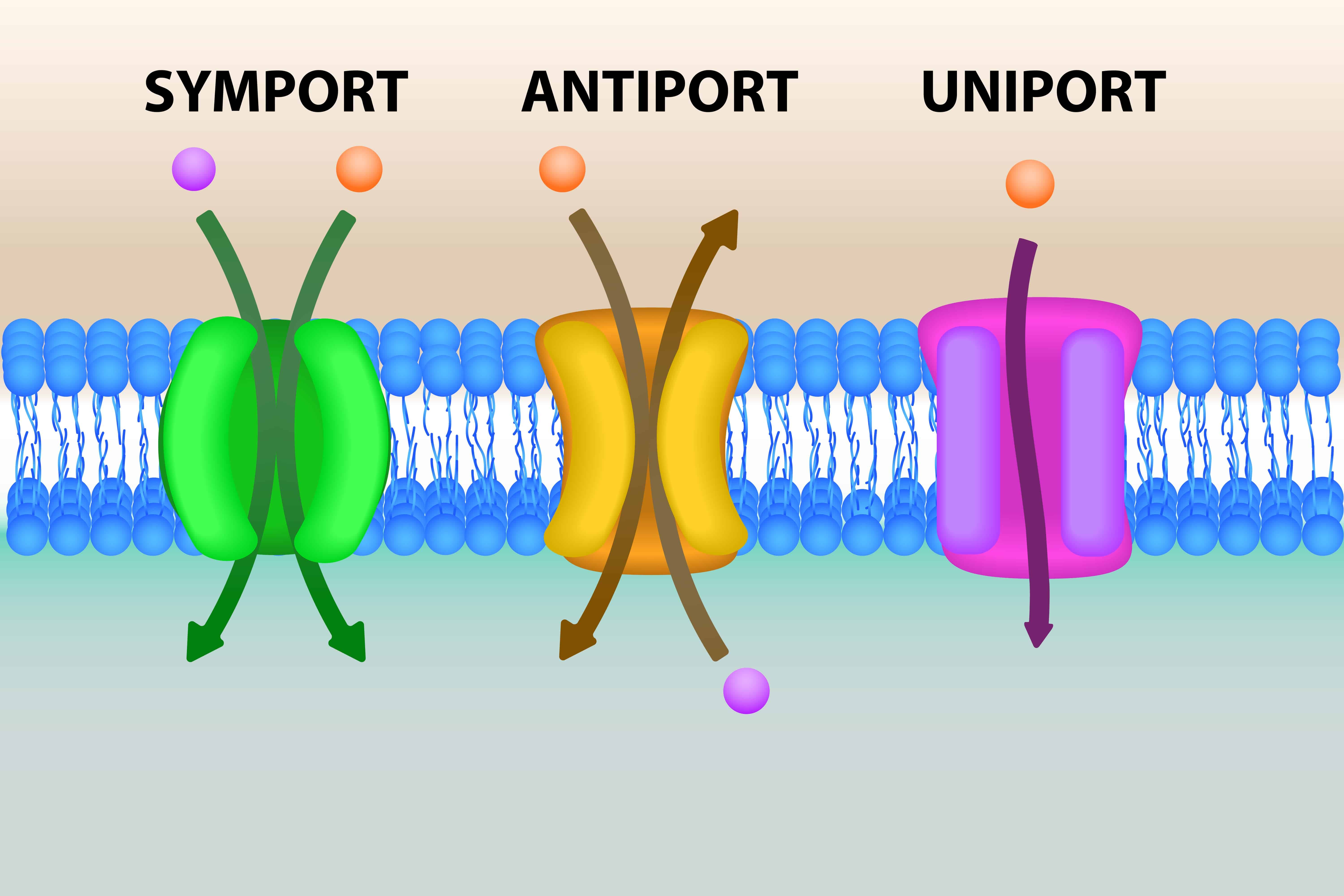
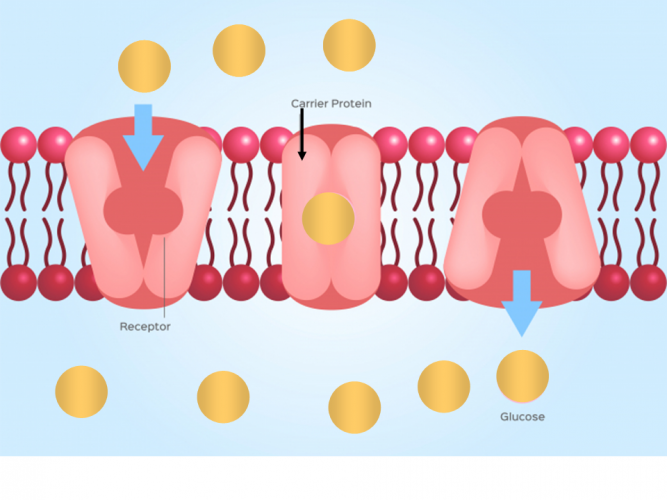
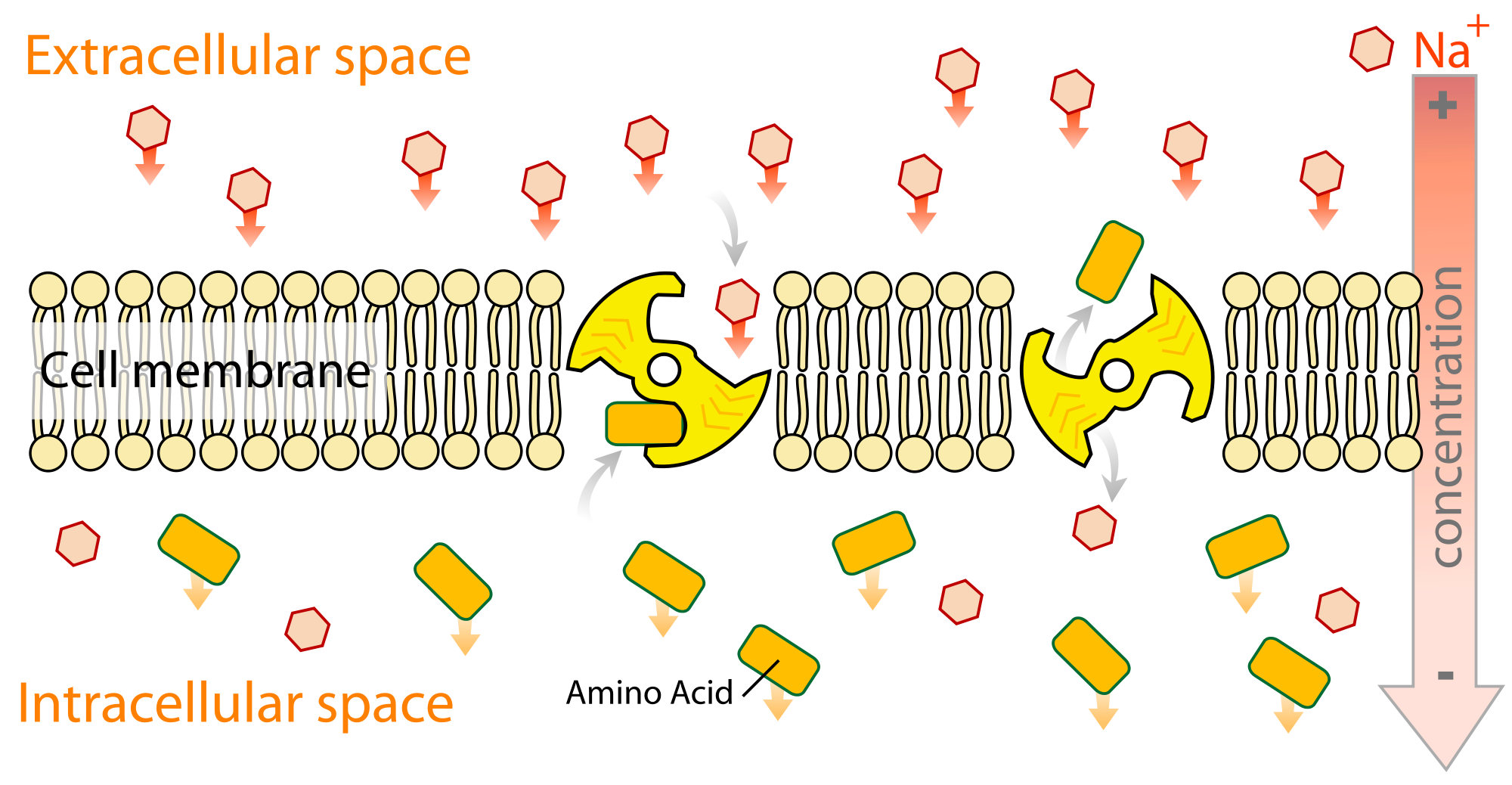
Channels channel proteins span the membrane and make hydrophilic tunnels across it, allowing their target molecules to pass through by diffusion. Cotransport (also known as symport) and exchange (also known as. The movement of substances through the cell membrane that requires energy. Web drawing pad quiz downloads 0:00 notes active transport movement of solutes against their electrochemical gradients extracellular space is positively charged intracellular space is negatively charged requires energy to overcome solute's gradient facilitated by transporters not channel proteins atp driven pumps primary active transport Web the drawing below shows the fluid inside and outside of a cell. Examples will include the diffusion of gases across alveolar. Web in secondary active transport, the movement of a driving ion down an electrochemical gradient is used to drive the uphill transport of another ion/molecule against a concentration or electrochemical gradient.
7 Different Types of Active Transport PopOptiq
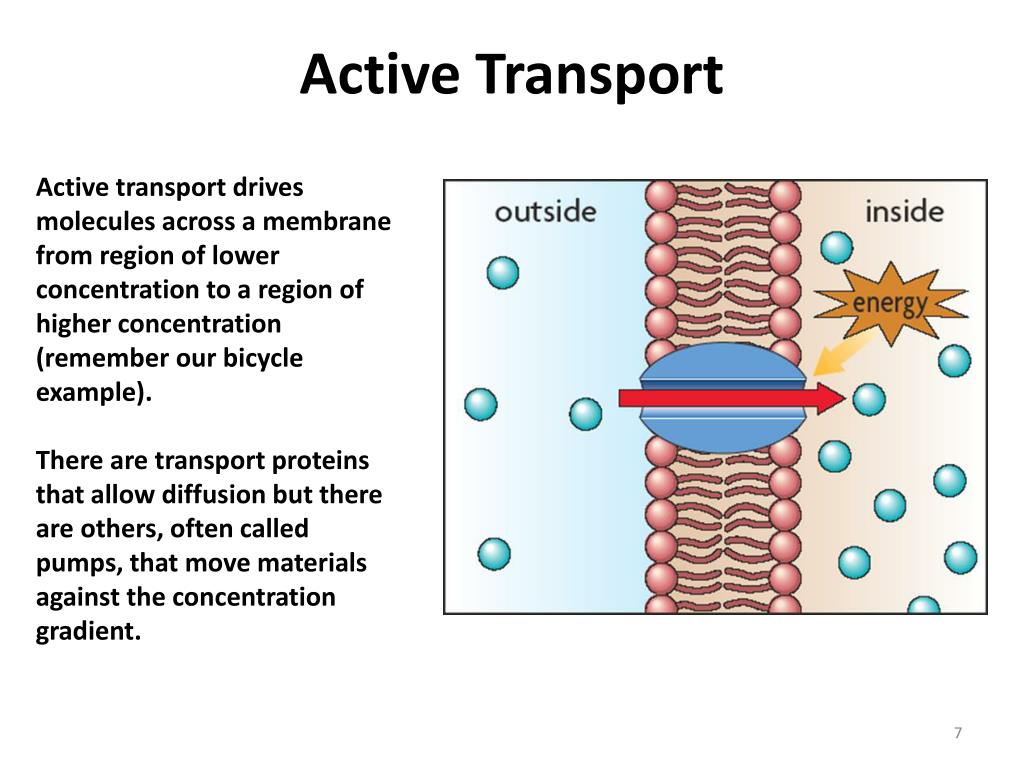
Web active transport uses energy to transport molecules across the plasma membrane. This is key to maintaining the resting membrane potential. Web there are two types of active transport: Web there are 2 main modes of transport of molecules across any biological membrane. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living.
Explain How Cells Use Active Transport Worksheet EdPlace
Abstract futuristic neon glowing concept car silhouette. Two types of secondary active transport processes exist: Web the drawing below shows the fluid inside and outside of a cell. Web primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on atp. Web browse 10,200+.
Active Transport And Diffusion In Plants
Web active transport is a highly demanding metabolic process; Web drawing pad quiz downloads 0:00 notes active transport movement of solutes against their electrochemical gradients extracellular space is positively charged intracellular space is negatively charged requires energy to overcome solute's gradient facilitated by transporters not channel proteins atp driven pumps primary active transport In contrast,.
Active Transport Diagram
Web active transport mechanisms may draw their enegy from the hydrolysis of atp, the absorbance of light, the transport of electrons, or coupling with other processes that are moving particles down their concentration gradients. Examples will include the diffusion of gases across alveolar. Instead, it is the movement of material due to the electrochemical gradient.
Process Of Active Transport In Root Hair Cells Plants Transport
They also use pumps to get molecules in or out of the cell. This uses energy from atp. If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular. Instead, it is the movement.
Anatomy & Physiology Active Transport ditki medical & biological
The dots represent molecules of a substance needed by the cell. Channels channel proteins span the membrane and make hydrophilic tunnels across it, allowing their target molecules to pass through by diffusion. Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). Cotransport (also known as symport).
PPT Active Transport PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2586036
Most popular 3d architecture abstract sports car speeding in urban highway city traffic of future experienced senior engineer consults young designer about project, Some cells can use up to 50% of their energy on active transport alone. No energy is necessary for this mode of transport. Instead, it is the movement of material due to.
Active Transport Across the Cell Membrane. Stock Vector Illustration
Cotransport (also known as symport) and exchange (also known as. Passive transport does not use energy to transport molecules across the membrane. Web there are two types of active transport: Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). The movement of substances through the cell.
Active Transport Tutorial Sophia Learning
Web primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on atp. In contrast, active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane using energy from adenosine triphosphate (atp). As you can see, transmembrane channels on either side of the pump allow.
What Molecule Is Necessary for Active Transport WadehasJohns
At activity end, administer the cell membrane quiz. However, the cell often needs to transport materials against their concentration gradient. The dots represent molecules of a substance needed by the cell. Web active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. Web active transport mechanisms may draw their enegy from the hydrolysis of atp,.
Active Transport Drawing Most popular abstract futuristic neon glowing concept car silhouette. Web active transport mechanisms may draw their enegy from the hydrolysis of atp, the absorbance of light, the transport of electrons, or coupling with other processes that are moving particles down their concentration gradients. Web active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. This exports three sodium ions in return for two potassium ions. Web in secondary active transport, the movement of a driving ion down an electrochemical gradient is used to drive the uphill transport of another ion/molecule against a concentration or electrochemical gradient.
Web In Secondary Active Transport, The Movement Of A Driving Ion Down An Electrochemical Gradient Is Used To Drive The Uphill Transport Of Another Ion/Molecule Against A Concentration Or Electrochemical Gradient.
This process is in contrast to passive transport , which allows molecules or ions to move down their concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to an area. At activity end, administer the cell membrane quiz. Web drawing pad quiz downloads 0:00 notes active transport movement of solutes against their electrochemical gradients extracellular space is positively charged intracellular space is negatively charged requires energy to overcome solute's gradient facilitated by transporters not channel proteins atp driven pumps primary active transport For all of the transport methods described above, the cell expends no energy.
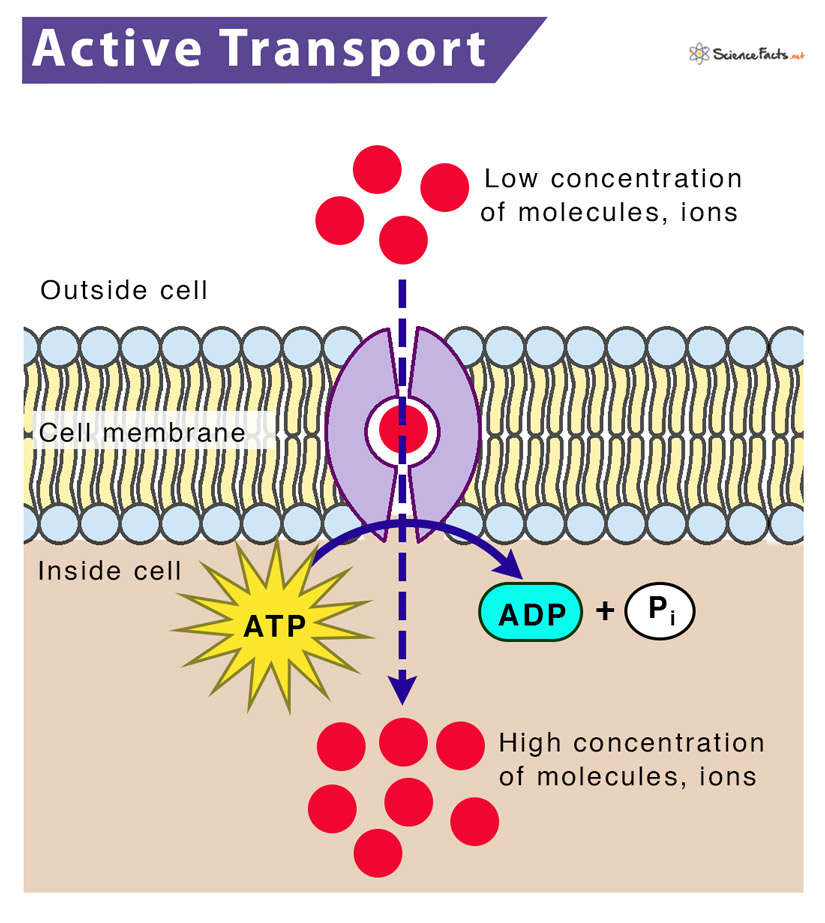
Web “Active Transport Is Defined As A Process That Involves The Movement Of Molecules From A Region Of Lower Concentration To A Region Of Higher Concentration Against A Gradient Or An Obstacle With The Use Of External Energy.” During The Process Of Active Transport, A Protein Pump Makes Use Of Stored Energy In The Form Of Atp, To Move.
During primary active transport, atp is required to move a substance across a membrane, with the help of membrane protein, and against its concentration. Web the drawing below shows the fluid inside and outside of a cell. Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). Figure 4.8.6 use this image to answer question #4
Primary Active Transport That Uses Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp), And Secondary Active Transport That Uses An Electrochemical Gradient.
Cotransport (also known as symport) and exchange (also known as. These are passive and active transport. If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular. Explain which type of transport — active or passive — is needed to move the molecules into the cell.
Web There Are Two Types Of Active Transport:
Web browse 10,200+ active transport drawing stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. This exports three sodium ions in return for two potassium ions. May 16, 2020 definition active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. Web primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on atp.